Blow molding (blow moulding), or plastic blow molding, is a fabricating process that companies use to create hollow plastic parts and products. It is named blow molding because it involves blowing compressed air into molten plastic so that it expands like a balloon and takes a particular shape. Read More…
No matter what your blow molding needs are Western Industries is ready to assist you. We believe in thinking outside the mold and using unique methods to come up with large-part blow molding solutions for our customers. We have access to state-of-the-art technology and over 100 years of combined experience serving a variety of industries. When you choose Western Industries, you have the Western...
With blow molding presses from 1 to 80 lbs., Iceberg Molding has the ability & resources for every step of your blow molding requirements - from a competitive part quote to part & product development support start to finish.
Founded in 1984, Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, Inc. is a turn-key manufacturer who offers custom blow molding and custom plastic injection molding for a variety of industries. With more than 35 years of experience, our quality products are unparalleled. We process an almost infinite variety of thermoplastic resins, our prices are competitive, our delivery is on time, and we offer superior customer...
Depend on the custom blow molders since 1978. ACM Plastic Products offers complete blow molding capabilities, including many specialty services like insert molding, painting, foaming, assembly & packaging – just name it! New product development & short runs through high volume production, our seasoned professionals put quality & cost efficiency first. Call us today for honestly the best...

EXI-plast is a full-service provider of custom plastic moulding services, specializing in blow moulded solutions for customers worldwide across a wide variety of industries. With over 30 years of experience developing, producing, and finishing custom plastic products, we have also become a sustainability leader through the integration of postconsumer resins. With products ranging from less than...
Since 1952, SPI Group has provided custom blow molding for a diverse range of industries, such as agricultural, plumbing, electronics, and more. Our team can meet your needs with a variety of plastics, such as HDPE, ABS, polycarbonate, and TPE. Secondary operations and assembly services are also available. SPI is a leader in our industry due to our customer-oriented ability to deliver successful...
At Cado Company, we specialize in delivering high-quality blow molding solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients. With years of experience in the industry, we have honed our expertise in producing durable, precise, and reliable blow-molded products.

At Western Case Incorporated, we focus on excellence in blow molding, producing custom plastic cases and components that are designed with precision and durability in mind. Our process allows us to create strong, lightweight products that combine functionality with consistent quality.

More Blow Molded Plastics Companies
What is Blow Molded Plastics?
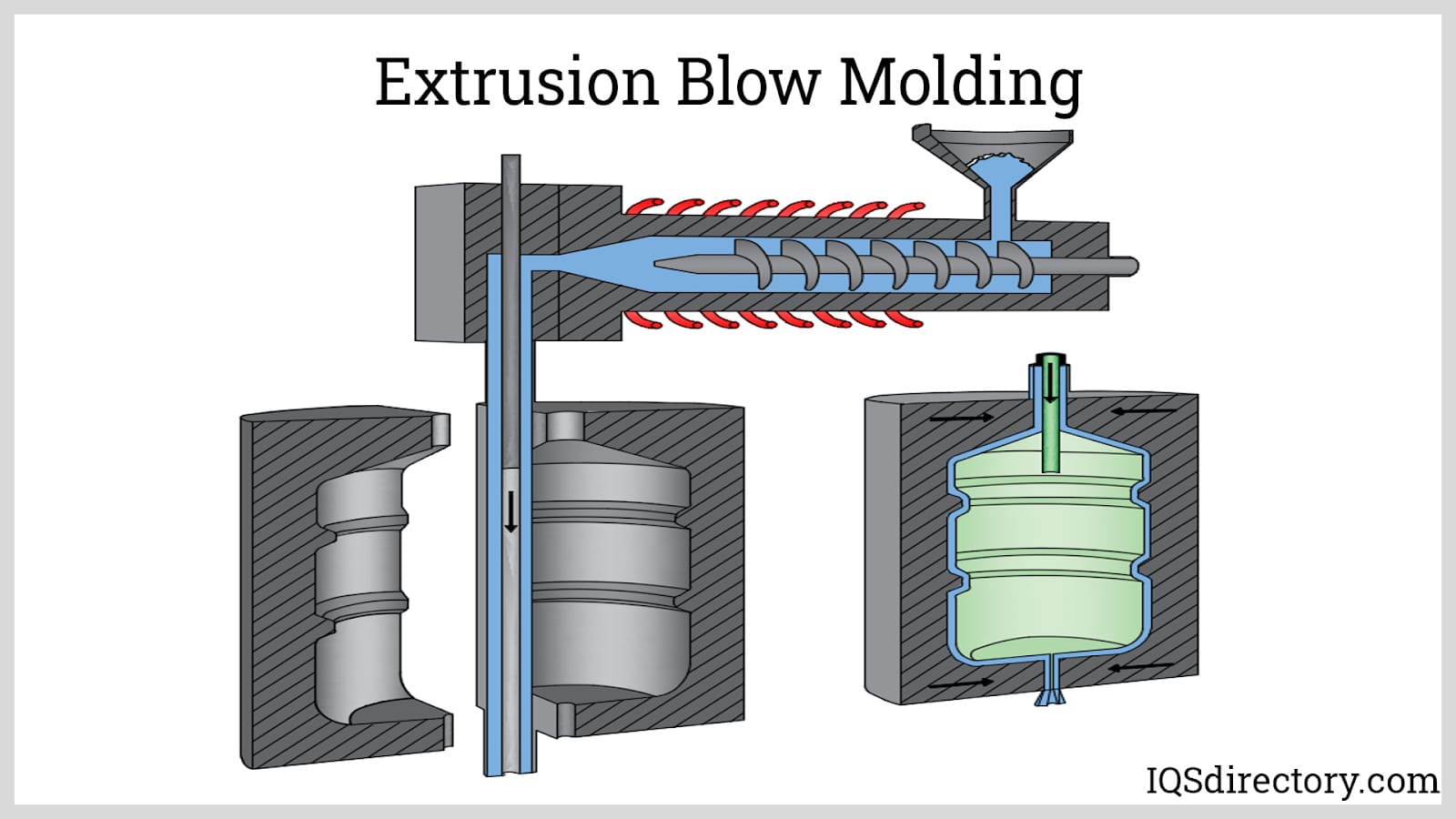
Blow molded plastics are hollow, lightweight plastic components produced through the advanced manufacturing technique known as blow molding. This process, fundamental to the plastics industry, is akin to inflating a balloon inside a precision-engineered mold—molten thermoplastic is transformed into bottles, containers, tanks, and complex hollow forms with uniform, thin walls. The blow molding process begins with a softened plastic tube (called a parison), which is clamped into a custom metal mold. Pressurized air—typically ranging from 25 to 150 PSI—is then injected, forcing the plastic outward until it adopts the mold’s exact shape. Once cooled and solidified, the mold opens, revealing a seamless, air-tight product ready for downstream applications.
Key Types of Blow Molding Processes:
- Extrusion Blow Molding: A continuous parison is extruded, making this process ideal for high-volume production of items like milk jugs, automotive fuel tanks, and industrial drums (often 1–5 gallons or larger). It supports the creation of containers with handles and other unique geometries.
- Injection Blow Molding: Here, pre-formed plastic is injected into a preform mold, then blown into its final shape. This method is favored for precision items such as medical vials, small pharmaceutical bottles, and single-use containers (typically under 500 ml).
- Stretch Blow Molding: PET preforms are both stretched and blown, which results in superior wall uniformity and clarity—making this process perfect for beverage bottles, especially high-clarity 2-liter soda bottles and water bottles.
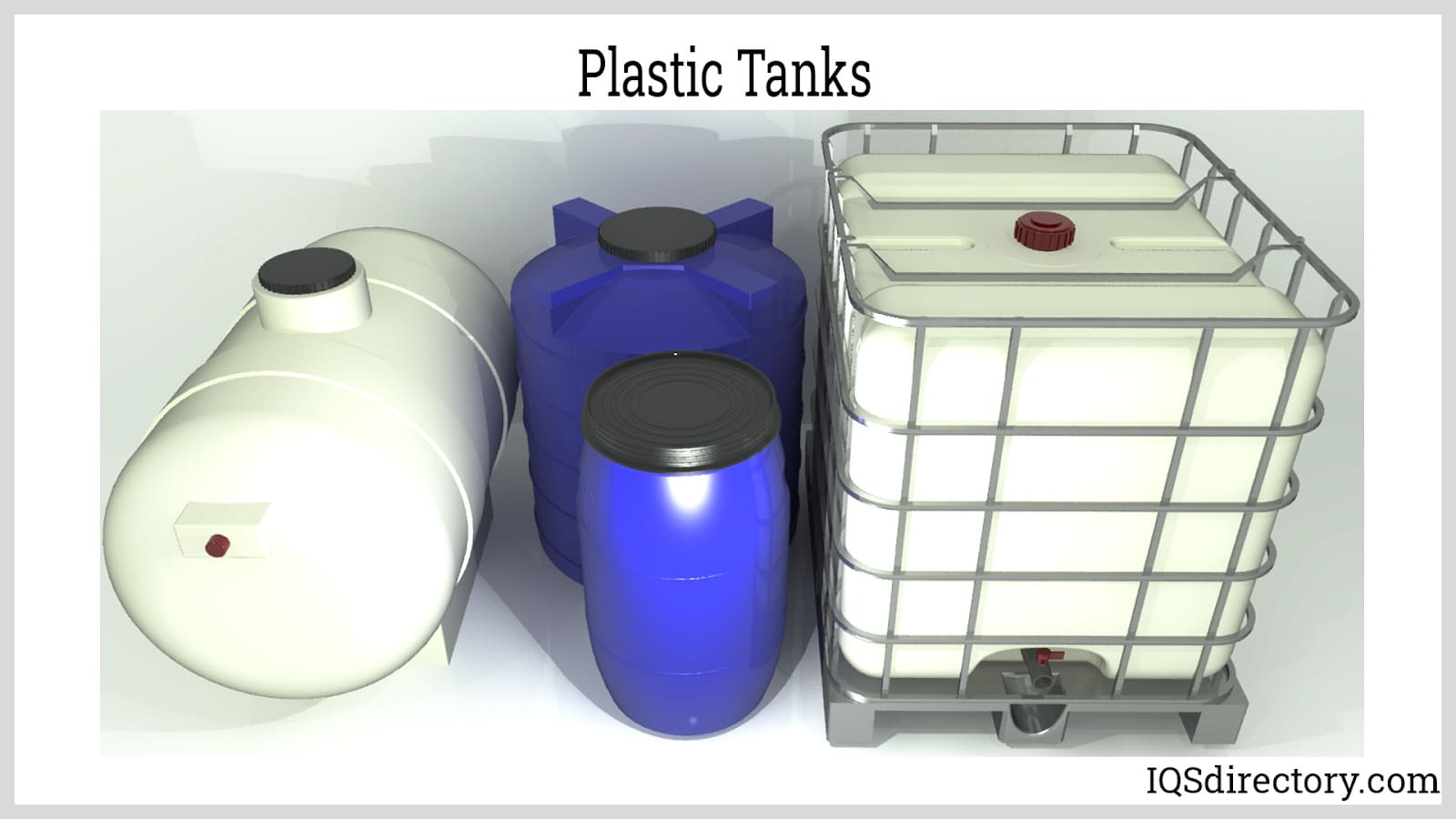
Common blow molding materials include polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). These robust, recyclable plastics are selected for their durability, chemical resistance, and adaptability, serving applications from shampoo and detergent bottles to automotive ducts and industrial tanks. Typical wall thicknesses range from 0.01” to 0.25”, striking a balance between strength and weight efficiency—a 1-gallon jug, for example, may weigh around 100 grams.
Blow molding is renowned for its speed and scalability, with cycle times between 20 and 60 seconds, enabling manufacturers to produce millions of units annually. Packaging applications constitute around 80% of all blow-molded output, but the process is also indispensable in creating industrial parts such as HVAC ducts, chemical storage drums, and custom shipping containers.
Manufacturers leverage blow molding to create smooth, seamless, and air-tight products that require no secondary assembly. These products are engineered to safely contain substances like herbicides, pesticides, cosmetics, automotive oils, chemicals, and food products. Industries benefiting from blow molded plastics include:
- Automotive and transportation (fluid reservoirs, ducts, toolboxes)
- Food and beverage (water bottles, juice containers, dairy packaging)
- Lawn and garden (planters, watering cans, compost bins)
- Waste management (recycling bins, garbage cans, 55-gallon drums)
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals (medical vials, specimen containers, inhalers)
- Consumer products (storage totes, cases, toy components)
- Office supplies (filing boxes, organizers, custom enclosures)
Looking to compare blow molding with other plastic forming processes? Explore the differences between blow molding and rotational molding to determine the best solution for your project.
History of Blow Molding
The origins of blow molding in manufacturing date to the early 20th century, inspired by traditional glass-blowing techniques. Adapted for plastics in the 1930s, the first patent for blow molding plastics was granted in 1938 to Enoch Ferngren and William Kopitke, whose innovations at Plax Corporation marked a pivotal shift. Using cellulose acetate, they demonstrated how hollow containers could be mass-produced efficiently.
The post-World War II era saw a surge in plastic use, especially with the widespread adoption of polyethylene. In 1947, John Wesley Hyatt introduced extrusion blow molding, revolutionizing the industry by enabling the cost-effective production of everything from bottles to automotive toys and tanks. This method extrudes a tube of molten plastic, which is then captured, inflated, and cooled to form durable, repeatable shapes.
The 1960s brought the advent of injection blow molding, facilitating even greater manufacturing precision and complexity, particularly for smaller, intricately detailed items such as pharmaceutical and laboratory vials. The method’s two-stage process—injection and blowing—improved consistency and part quality.
In the 1970s, stretch blow molding emerged, especially significant for the beverage industry. The development of PET (polyethylene terephthalate) bottles—famous for their clarity, strength, and lightweight—transformed beverage packaging worldwide. This era also marked the rise of automated blow molding lines, enhancing efficiency, product consistency, and customization potential.
Today, blow molding technology continues to evolve, integrating automation, computer-aided design, and sustainable manufacturing practices. The versatility and efficiency of blow molding ensure its integral role in producing diverse consumer products, industrial components, and packaging solutions.
What polymers are used in blow molded plastic manufacturing?
Answer: Blow molded plastics depend on a select group of polymers, each chosen for its unique blend of flexibility, chemical resistance, durability, and processability in blow molding operations. Selecting the right polymer is critical for performance, regulatory compliance, and end-use application. Here’s a detailed look at the most commonly used polymers:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
This workhorse polymer delivers exceptional durability and chemical resistance, making it the industry standard for milk jugs, detergent bottles, fuel tanks, and industrial drums. With a tensile strength of 3,000–4,500 PSI, HDPE is suitable for everything from 1-gallon to 55-gallon containers. It’s also FDA-approved for food contact and easily recycled, supporting sustainable manufacturing goals. - Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE):
LDPE is softer and more flexible than HDPE, fitting squeezable applications such as condiment bottles and cosmetic tubes. Although its lower tensile strength (1,200–2,000 PSI) limits its use for heavier-duty containers, its flexibility is ideal for thin-walled, easy-dispense packaging. - Polypropylene (PP):
Renowned for high heat resistance (up to 220°F) and remarkable toughness, PP is frequently used for automotive reservoirs, reusable food storage containers, and laboratory equipment. Its excellent chemical resistance and rigidity (tensile strength around 3,500 PSI) make it a versatile option for both industrial and consumer applications. - Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET):
PET is the material of choice for clear beverage bottles and food packaging due to its outstanding clarity, gas and moisture barrier properties, and strength (up to 8,000 PSI). Used primarily in stretch blow molding, PET delivers lightweight, impact-resistant bottles for water, soda, juice, and personal care products. - Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC):
Although less common in mainstream packaging, PVC stands out for its rigidity, chemical resistance, and ability to form tough containers and pipes. Its blow molding applications often center on industrial, chemical, and automotive parts, where strength and resistance to corrosion are priorities. - Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS):
ABS features high impact resistance (5,000 PSI) and is used for more demanding parts such as tool cases, automotive ducting, and specialty enclosures. While more expensive than basic polyolefins, ABS is chosen for applications requiring a blend of toughness, dimensional stability, and high-quality surface finishes.
These polymers are typically processed at melt temperatures between 300°F and 500°F and are compatible with extrusion, injection, or stretch blow molding methods. Their versatility supports the production of items ranging from tiny medical vials to large, heavy-duty industrial drums.
Curious about which polymer best fits your application? Ask a plastics engineer or supplier about the optimal material for your specific performance, compliance, and sustainability requirements.
Blow Molding Process
Blow molding is a highly adaptable manufacturing technology for producing a wide variety of hollow plastic products. The primary types—extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding—all follow fundamental steps, though each has unique variations to suit specific applications.
- Melting and Forming the Plastic: The process starts with melting pellets or granules of plastic resin, which are then shaped into a preform or parison using either extrusion or injection molding. The parison is a cylindrical, tube-like piece with an open end designed for air injection. The precise control at this stage determines the wall thickness and overall quality of the finished product.
- Clamping into the Mold Cavity: The hot, pliable parison or preform is placed between the two halves of a metal mold, which closes to define the final product’s shape and features (such as threads, handles, or logos).
- Introducing Air Pressure: Air is blown into the parison via a blow pin or needle, causing it to expand and perfectly conform to the mold’s contours. This step is critical for achieving uniform wall thickness and structural integrity.
- Cooling the Product: The newly formed product is rapidly cooled, often with water circulating through the mold or by conduction. Some specialized processes use evaporative fluids or chilled molds for faster cycle times. Blow molding machines are capable of producing up to 20,000 containers per hour in high-volume operations.
- Ejecting the Final Product: Once the plastic has cooled and set, the mold opens and the finished part is ejected, ready for trimming, quality control, and secondary operations (if needed).
This streamlined process enables rapid, consistent, and cost-effective production of hollow plastic parts for a broad range of industries. Whether you need high-volume packaging or custom industrial components, blow molding delivers unmatched scalability and flexibility.
Want to see the process in action? Watch a blow molding demonstration video or request a factory tour from a leading blow molding manufacturer.
Blow Molding Design
Designing a custom blow molded product requires careful coordination between material selection, process type, and mold cavity geometry. These decisions are dictated by the customer’s unique performance, appearance, and regulatory requirements.
- Material Choice: The intended use—be it chemical storage, food packaging, or automotive—determines the most suitable polymer. For example, products needing high compaction resistance might specify engineered resins like polysulfone or specialty blends.
- Process Selection: The choice between extrusion, injection, or stretch blow molding depends on part size, complexity, required clarity, and production volume.
- Mold Design: Standard molds are available for common containers and jars, offering speed and cost savings. For custom applications, manufacturers develop bespoke tooling, beginning with CAD models, 3D printed prototypes, and customer feedback before investing in steel molds.
While custom blow molding typically involves longer lead times and upfront costs, it results in products that precisely match your requirements—whether that means unique shapes, integrated handles, embossing, or brand-specific colors. Standard molds, on the other hand, are ideal when budget or lead time is limited.
Wondering how to optimize your product design for blow molding? Request a design consultation or submit a CAD file to a blow molding specialist for feedback on manufacturability, cost, and performance.
Variations in Blow Molding Processes
Understanding the different blow molding methods helps you select the right process for your application:
- Extrusion Blow Molding: The most straightforward technique, extrusion blow molding extrudes a tube of molten plastic (parison) that is then captured in a mold and inflated. It accommodates a wide range of sizes and shapes, including containers with handles and complex geometries. This method exclusively produces hollow products and usually results in a mold seam down the product’s center.
- Injection Blow Molding: Combining injection and blow molding, this process starts with an injection-molded preform, which is then transferred to a blow mold for inflation. It is best suited for small, high-precision containers like medicine bottles, but generally cannot create parts with handles.
- Stretch Blow Molding: This category includes:
- Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM): Used for premium bottles (e.g., liquor, water, peanut butter jars), ISBM creates preforms via injection molding, then reheats and stretches them before inflation. This method produces strong, clear, and dimensionally consistent containers, ideal for high-end beverage packaging.
- Reheat and Blow Molding (RHB): Cost-effective and flexible, RHB uses pre-made preforms purchased from suppliers. These are reheated, then blow molded into final shapes, making the process accessible for smaller or faster-changing production lines.
Need help choosing between extrusion, injection, or stretch blow molding? Compare blow molding processes for your industry or product by contacting an expert or browsing detailed case studies.
Benefits of Blow Molding
The blow molding process provides a unique combination of advantages for industrial and commercial manufacturing:
- Cost Efficiency: Minimal tooling requirements and high-output cycle times make blow molding more economical than injection molding for hollow parts. Tooling costs are typically lower, and the process is ideal for both short and long production runs.
- Design Flexibility: Blow molding supports intricate shapes, integrated handles, threads, and embossing, enabling creative freedom for industrial designers and product engineers.
- High-Speed Production: With cycle times as short as 20–60 seconds and the ability to run 24/7, blow molding delivers millions of units per year for demanding markets like food, beverage, and automotive.
- Material Versatility: Compatible with a range of thermoplastics—including HDPE, LDPE, PP, PET, and specialty resins—blow molding meets diverse industry standards, including FDA, NSF, and automotive OEM specifications.
- Seamless, Airtight Products: The process produces leak-proof, one-piece containers that eliminate the need for secondary assembly or welding.
- Sustainability: Many blow molded products are recyclable, supporting circular economy initiatives and reducing environmental impact.
However, blow molding may face challenges such as achieving perfectly uniform wall thickness (rotational molding may be preferable in some cases) and occasional risk of minor leaks or pinholes if process controls are inadequate.
Interested in maximizing cost savings or improving sustainability? Request a quote for recycled-content blow molded products or compare total cost of ownership between blow molding and competing processes.
How to select a blow molded plastic supplier?
Answer: Selecting the right blow molded plastic supplier is critical to the success of your project—whether you’re sourcing beverage bottles, chemical tanks, or custom-engineered parts. Here’s a comprehensive guide to making an informed decision. Please use our RFQ to send requirements to up to 6 suppliers.
- Identify Your Needs:
Define the product—determine size (from 500 ml bottles to 55-gallon drums), polymer type (HDPE, PET, PP), and process method (extrusion, injection, or stretch blow molding). Outline volume requirements (10,000 units or 1 million annually?), clarity, color, and any special features (e.g., handles, embossing, tamper-evident lids). - Check Experience and Specialization:
Evaluate suppliers with a proven track record in your industry—whether you need food-grade PET bottles or industrial tanks. Years in business, relevant certifications, and a robust client list (10+ years is a good benchmark) indicate reliability and expertise. - Evaluate Production Capacity:
Confirm the supplier can meet your demand and delivery schedule. Inquire about machine sizes (1–500 liter molds), lead times (2–6 weeks), and flexibility for scaling up production or accommodating rush orders. - Assess Material Quality:
Ensure suppliers use only virgin or certified food-grade resins (e.g., HDPE with 0.95 g/cm³ density, BPA-free PET). Ask for proof of FDA, NSF, or ISO 9001 certifications. Request product samples to test for wall thickness, weight, and mechanical performance. - Verify Customization Options:
If you need custom branding, unique shapes, or special features, prioritize suppliers with in-house mold design and prototyping capabilities. Inquire about mold costs (often $1,000–$10,000) and typical turnaround times for custom tooling. - Compare Costs and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs):
Obtain detailed quotes—bulk HDPE bottles may cost as little as $0.10 each, while specialty PET runs could be $0.50 or more per unit. Match supplier MOQs (1,000–100,000 units) to your projected needs. - Gauge Reliability and Support:
Review online feedback, ask for customer references, or check industry forums. Responsive communication, transparent pricing, and a history of on-time delivery are key indicators of a trustworthy partner.
Shortlist three to five suppliers, request product samples, and select the partner that best balances quality, cost, and speed for your application.
To make a fully informed choice:
- List your detailed technical and aesthetic requirements.
- Review company profiles in our directory of blow molded plastics manufacturers.
- Contact three or four suppliers individually to discuss your project, clarify expectations, and address all questions.
- Compare proposals, evaluate responsiveness, and choose the manufacturer offering the best fit for your schedule, budget, and quality needs.
Need help getting started? Request quotes from multiple suppliers or consult our blow molding experts for personalized recommendations.
Check out our Plastic Bags website
Check out our article on What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Blow Molding Compared to Rotational Molding?
FAQs and Buyer Resources
- What are the environmental benefits of blow molded plastics?
Many blow molded products are fully recyclable, and advances in bioplastics and post-consumer resin (PCR) are making this process even more sustainable. Ask your supplier about recycled-content options to reduce your carbon footprint. - How can I ensure product quality in blow molded parts?
Look for suppliers with robust quality control systems—such as in-line vision inspection, ultrasonic thickness testing, and ISO certifications—to minimize defects and ensure compliance with industry standards. - What are typical lead times for custom blow molded projects?
Depending on mold complexity and order size, lead times range from 2–6 weeks. Prototyping and mold development may add time upfront but result in better long-term value. - Can blow molded plastics be used for hazardous or food-grade applications?
Yes, with the correct choice of certified resins (food-safe HDPE, FDA-approved PET), blow molded containers are ideal for food, beverage, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. Always request documentation of compliance. - How does blow molding compare to injection or rotational molding?
Blow molding is preferred for hollow, seamless parts with high-volume requirements. Injection molding is best for solid parts with intricate details; rotational molding excels at very large or double-walled containers. Read our in-depth comparison. - What secondary operations are available for blow molded products?
Options include trimming, drilling, printing, labeling, and assembly. Discuss your post-molding needs with suppliers to streamline your production workflow.
Ready to take the next step?
- Request a quote for your next blow molded plastics project.
- Download a material selection guide for blow molding applications.
- Contact an engineer to discuss custom mold design, prototyping, and production scaling.
- Explore our directory of top-rated blow molded plastics manufacturers and suppliers.
Empower your supply chain with the right blow molding partner. Whether you’re developing new packaging, optimizing an existing product line, or seeking innovative plastic solutions, blow molded plastics deliver unmatched value, versatility, and performance.
What is blow molded plastics?
Blow molded plastics are hollow, lightweight plastic components manufactured using the blow molding process. This involves inflating a softened plastic tube (parison) inside a mold with pressurized air, shaping it to make products like bottles, containers, tanks, and more. The technique creates seamless, airtight products ideal for packaging, industrial, and custom applications.
Which polymers are commonly used in blow molded plastic manufacturing?
The most common polymers used in blow molding are high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Each polymer is selected for unique properties like durability, chemical resistance, clarity, and flexibility, and is processed according to the part’s specific requirements.
What are the main types of blow molding processes?
The main types are extrusion blow molding (for items like milk jugs and industrial drums), injection blow molding (for small, precise containers like medical vials), and stretch blow molding (especially for clear beverage bottles). Each method involves different steps and is chosen based on part geometry, clarity, and production needs.
What industries use blow molded plastics?
Industries benefiting from blow molded plastics include automotive and transportation (fluid reservoirs, ducts), food and beverage (bottles, packaging), lawn and garden (watering cans, planters), waste management (recycling bins, drums), healthcare and pharmaceuticals (vials, containers), consumer products (storage totes, toys), and office supplies (boxes, organizers).
What are the advantages of blow molding?
Blow molding offers cost efficiency, design flexibility, high-speed production, and material versatility. It can create seamless, airtight products in a wide range of shapes and sizes, often at lower tooling costs compared to other plastic forming methods. Many blow molded products are also recyclable, supporting sustainability goals.
How do I select a blow molded plastics supplier?
Select a supplier by identifying your product requirements, checking their experience, evaluating production capacity, verifying material quality, assessing customization options, comparing costs and minimum order quantities, and gauging reliability and support. Requesting samples and reviewing certifications can help ensure you find a reliable, high-quality partner for your application.
Can blow molded plastics be used for food-grade or hazardous applications?
Yes, blow molded plastics are suitable for both food-grade and hazardous material applications when manufactured with certified resins such as food-safe HDPE or FDA-approved PET. Always request compliance documentation to ensure products meet the necessary regulatory standards.







 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators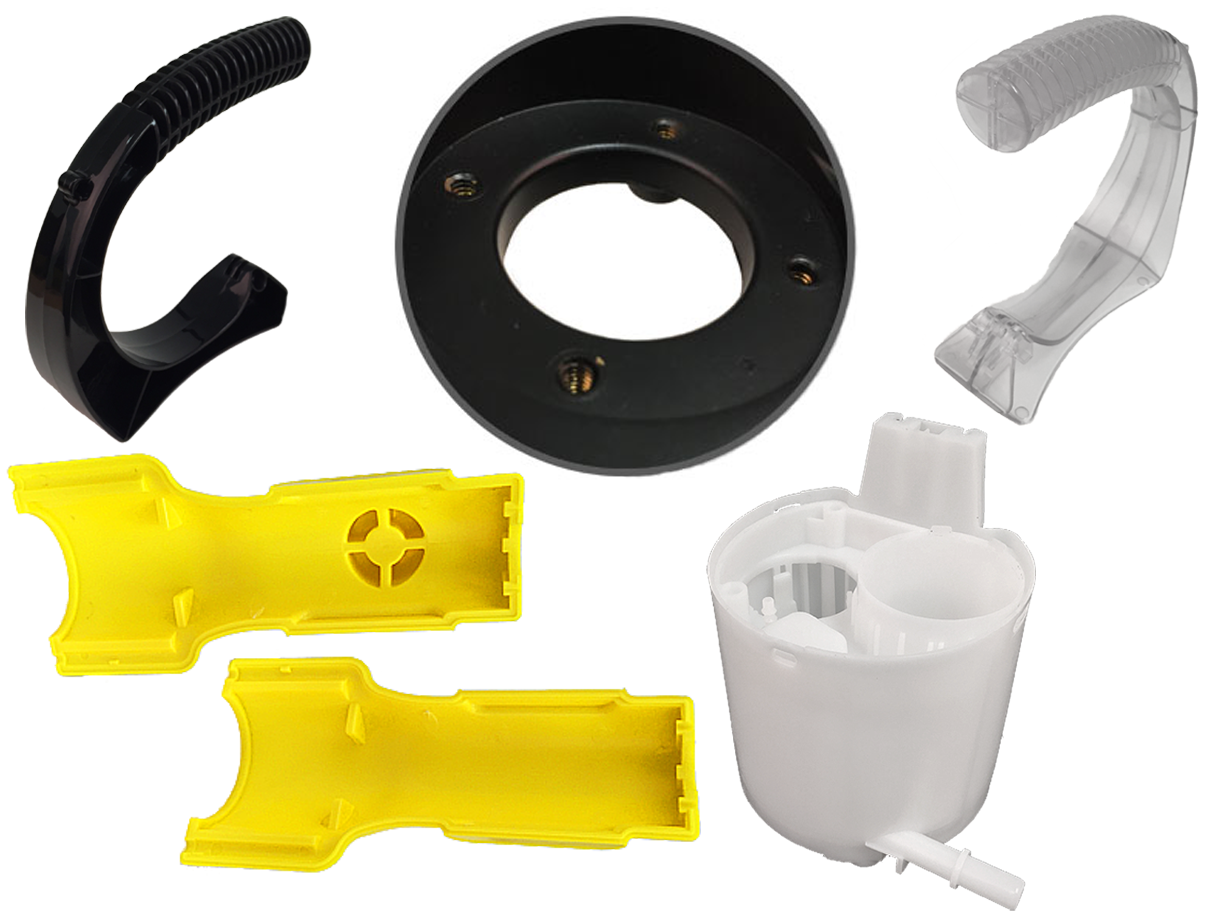 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics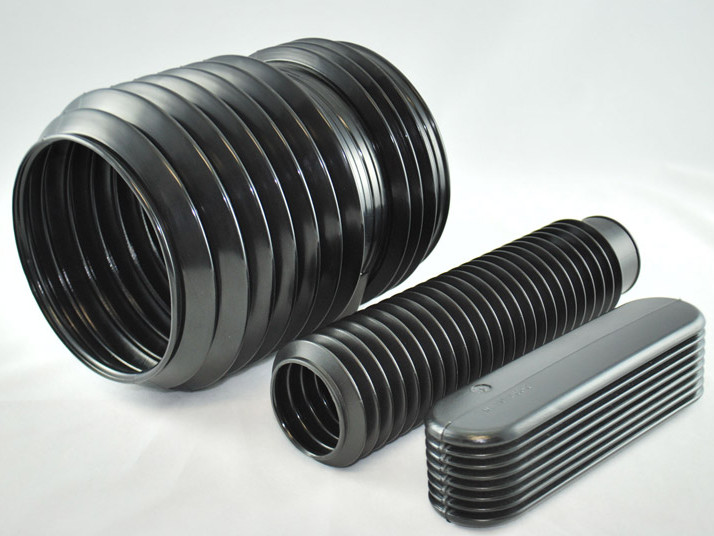 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding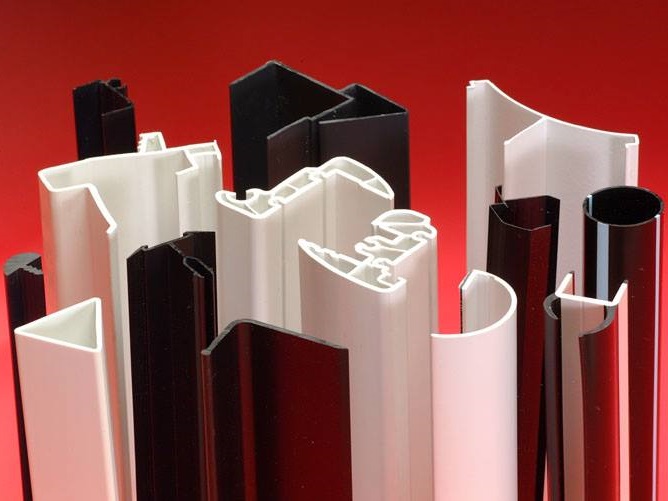 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding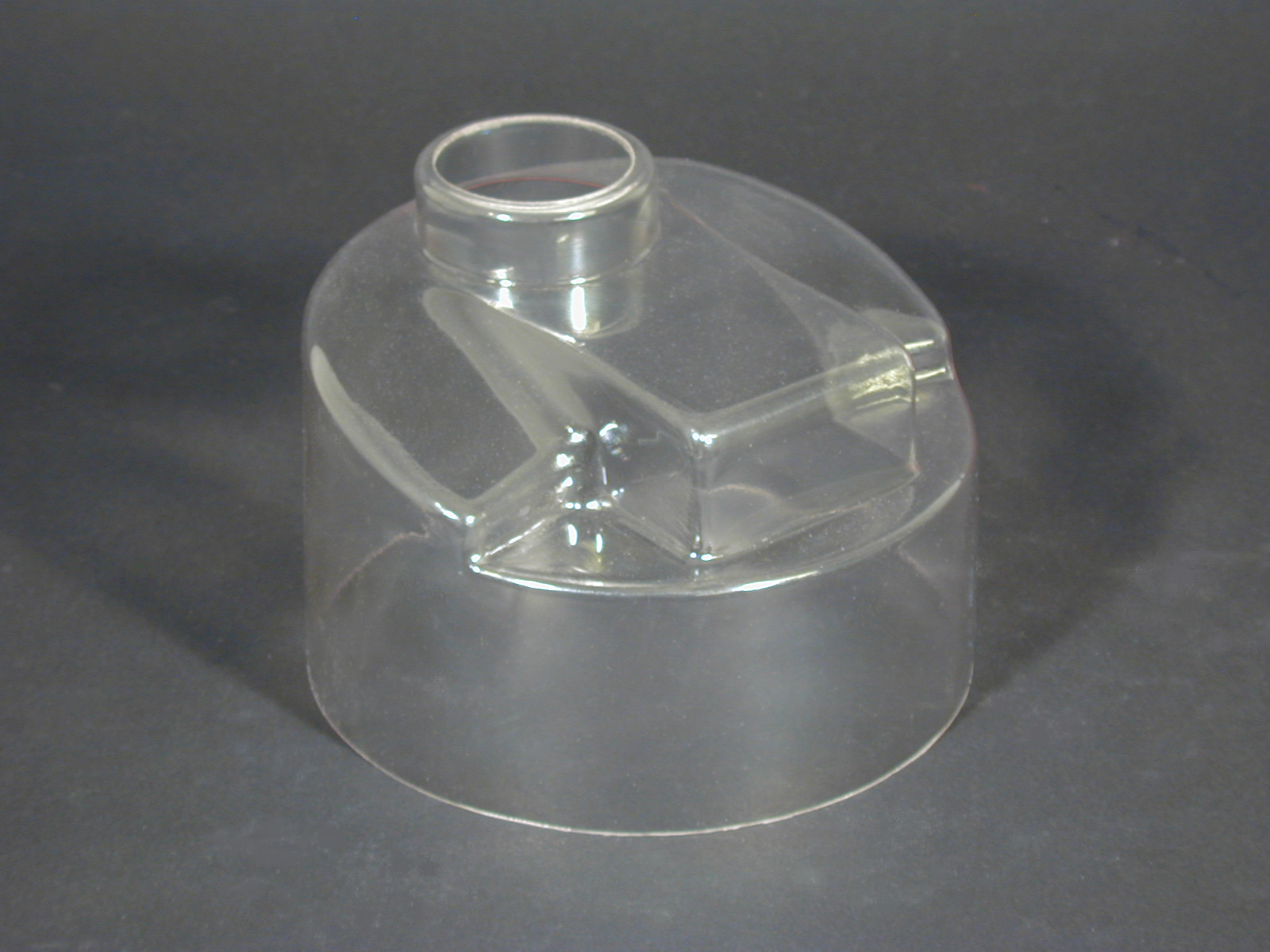 Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services